Strategy
July 2023
Mobile Apps vs Web Apps: What’s the Best Platform for My Business?

Companies worldwide, from ambitious start-ups to established corporations, are leveraging technology to drive growth, foster customer relationships, and stay competitive. A crucial aspect of this digital shift is the adoption of applications, more specifically, mobile and web apps.
As a software development agency, we often find businesses grappling with the dilemma of choosing between a mobile app and a web app. This choice is far from trivial, as it has significant implications for your company's operational efficiency, customer engagement, and overall growth trajectory. The decision, however, isn't about choosing the 'best' type of app in a general sense but about identifying the right solution for your specific business needs.
In this blog, we'll delve into the fundamental differences between mobile apps and web apps, examine their respective advantages and disadvantages, and explore various factors to consider when deciding the most appropriate platform for your business application. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge you need to make an informed choice that aligns with your business objectives, customer behaviour, and technological trends.
But remember, when it comes to software development, one size does not fit all. Whether you opt for a mobile or web app, the decision should resonate with your unique business requirements, target audience, and long-term growth strategy. So, let's explore mobile apps vs web apps and which is better for your business.
What is a Mobile App?
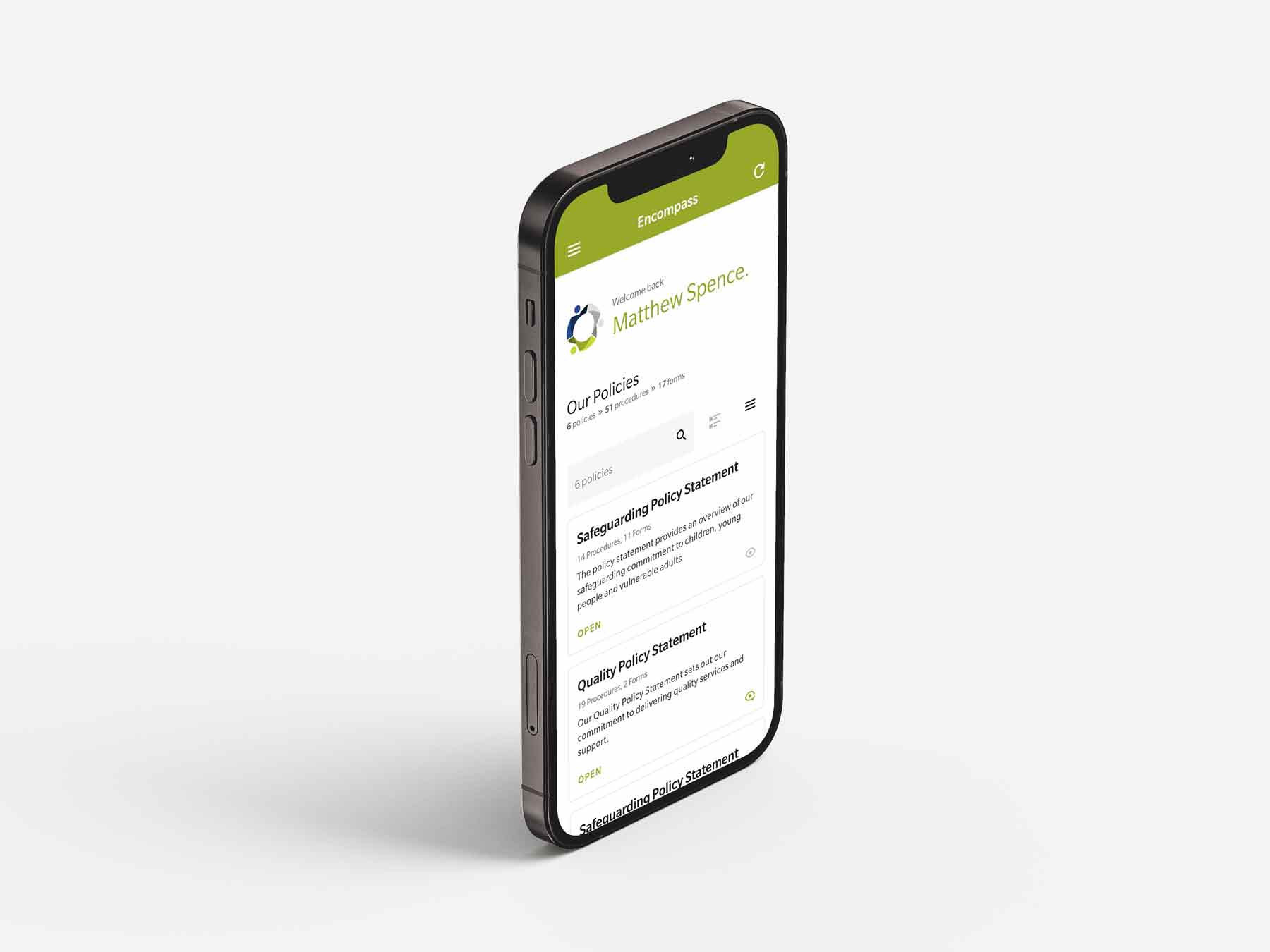
A mobile app, short for mobile application, is software designed to run on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, that provide users with services similar to those accessed on PCs but optimised for the mobile experience.
Mobile apps are developed specifically for individual operating systems like iOS (Apple's mobile operating system) or Android. This platform-specific development is crucial because it ensures the app will function optimally on the device's native platform, offering an enhanced user interface (UI) and user experience (UX).
If you're interested in the potential possibilities of building a mobile app and would like to explore a potential use case, make sure to check out our case study on how we worked with Encompass to simplify their procedure with a mobile app.
Native Apps.
Native apps are developed specifically for a certain platform or operating system (OS) such as Android or iOS. Native applications are known for their superior app performance and user experience tailored to the platform’s UX.
Native apps can fully leverage device features like the camera, accelerometer, or push notifications, but they require more time and skill to develop.
Cross-Platform Apps.
As businesses aim to engage audiences across various devices and operating systems, the concept of 'Cross-Platform Accessibility' becomes highly relevant. A cross-platform app is a type of software application that’s compatible with multiple operating systems, meaning it can run on any platform without requiring separate versions for each.
The main advantage of cross-platform apps is their 'write once, run anywhere' attribute. The same codebase can be used to deploy the app on different platforms, resulting in significantly reduced development time and cost compared to native app development where separate codebases are required for each platform. However, while cross-platform apps have made tremendous strides in recent years, they may not always be able to fully leverage specific device or platform features the way native apps can. This could potentially result in minor compromises on performance or user experience.
Hybrid Apps.
Hybrid apps are a blend of native and web apps. They are written using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and are then encapsulated within a native application shell. This makes them able to function across platforms while still accessing some device-specific features.
Mobile apps can serve various functions, from providing entertainment (like gaming apps) and facilitating communication (messaging or video-calling apps), to serving as tools for personal organisation (productivity or health-tracking apps), or even assisting in complex business operations (project management or CRM apps).
In the context of businesses, mobile apps offer a strategic advantage by facilitating direct communication and engagement with customers. With features like push notifications, businesses can effectively reach their audience with updates, offers, and more. They also allow businesses to offer a more personalised user experience, which can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and retention.
The development and distribution of mobile apps are made possible through platforms like Apple's App Store for iOS apps and Google's Play Store for Android apps. These platforms provide developers with comprehensive guidelines and tools for development, while users can easily search for, download, and update the apps they wish to have on their devices.
Given their widespread use and versatility, mobile apps have become a critical component of a business's digital strategy. The choice of creating a mobile app, however, should be driven by the business's specific needs and its customers' behaviour.
The Pros and Cons of Developing Mobile Apps for Business.
App development for business is a significant step, and it's crucial to understand the advantages and drawbacks that come with it. Here, we delve into the pros and cons of mobile app development.
What are the Pros of Developing a Mobile App:
- Enhanced User Experience: Mobile apps usually offer a superior user experience compared to web apps. They are faster, more responsive, and can be designed with a UI/UX that's consistent with the operating system's look and feel.
-
Leverage Device Capabilities: Mobile apps can utilise device features like a camera, GPS, accelerometer, and push notifications. This can enhance functionality and user interaction, making the app more intuitive and enjoyable.
-
Offline Accessibility: Unlike most web apps, mobile apps can function offline. This can be a significant advantage if your target audience resides in areas with poor internet connectivity or if your app offers features that need to function offline.
-
Brand Presence: A mobile app puts your brand on your users' devices, serving as a constant reminder of your brand, enhancing visibility, and customer loyalty.
-
Personalisation: Mobile apps can offer higher levels of personalisation based on user behaviour, preferences, location, and more. This can lead to better user engagement and satisfaction.
What are the Cons of Developing a Mobile App?:
- Cost: The cost of app development is a defining factor for most businesses. Mobile apps, particularly native apps, tend to be more expensive to develop due to their platform-specific development process. They also require more time for development and testing, particularly if you plan to launch your app on both iOS and Android platforms.
-
Time-Consuming: Mobile apps typically take longer to develop than web apps. Additionally, if you’re developing a native app, you’ll need to create separate versions for iOS and Android, which can further extend the development timeline.
-
App Store Approval: To distribute a mobile app, you need to submit it for review and approval on app stores like Google’s Play Store or Apple’s App Store. This can be a lengthy process, and there’s always the chance your app may initially be rejected.
-
Updates: For users to benefit from app updates, they must download them, which can lead to inconsistencies if some users fail to update, and it’s harder to manage compared to web apps where updates are immediate and universal.
-
Competition: With millions of apps available in app stores, getting your app to be discovered can be challenging. You’ll need a solid app store optimisation (ASO) and digital marketing strategy to stand out.
In conclusion, the decision to develop a mobile app for your business should be well-informed, taking into account the specific needs of your business, your budget, and your target audience's preferences. At the end of the day, a well-designed and well-implemented mobile app can provide immense value to both your business and your users.
What is a Web App?
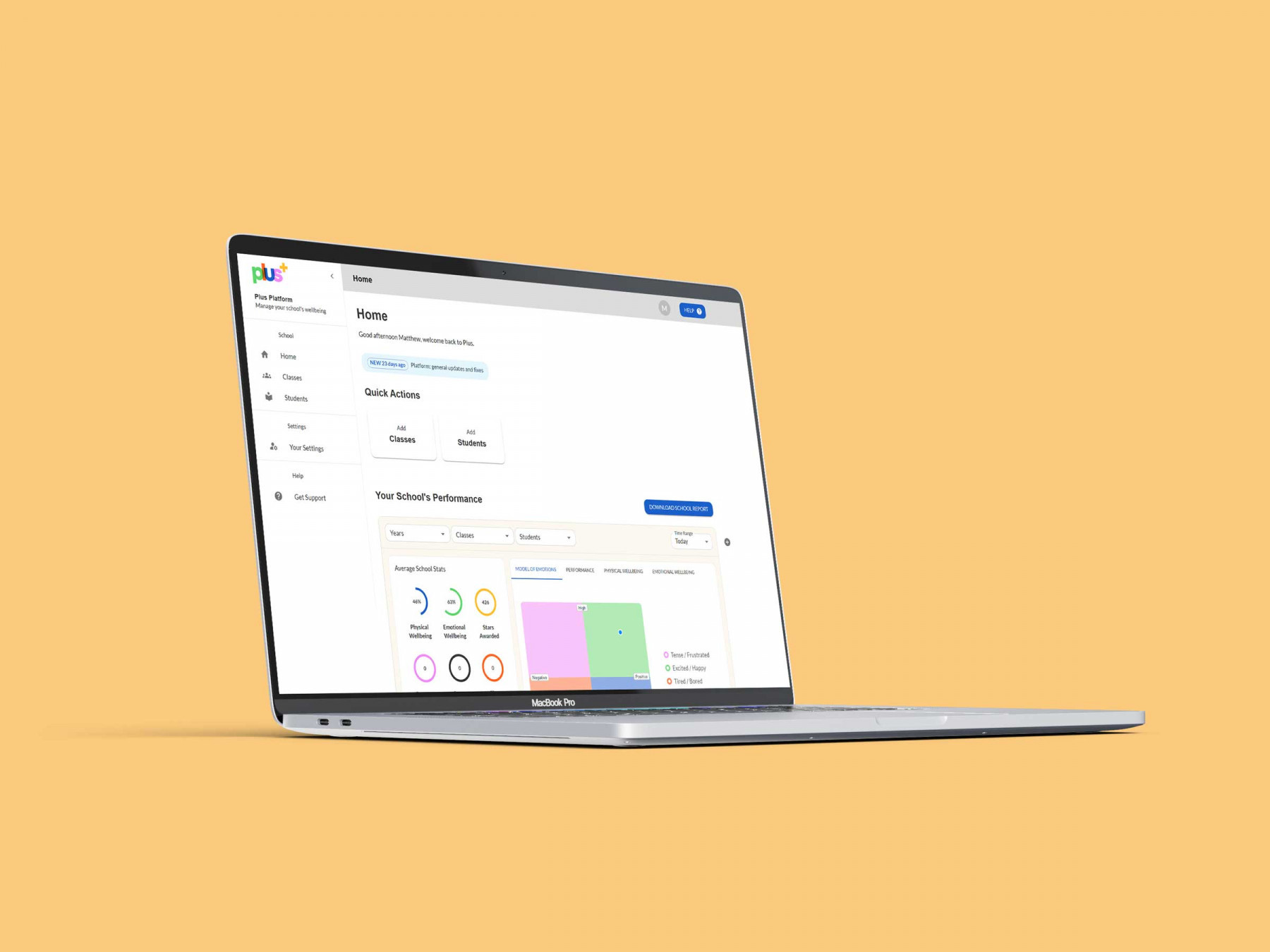
A web app is software that runs on a web server and doesn't need to be downloaded or installed, saving device storage and bypassing the need for update downloads. Unlike traditional websites, which primarily provide static content, web apps are interactive and allow for user engagement. However, they typically require an internet connection to function optimally, and their access to device-specific features can be limited compared to mobile apps.
Web apps are accessed through web browsers like Google Chrome, Safari, or Firefox, meaning they are not platform-specific and can be used on various devices, from PCs to smartphones. They are typically built using languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and can also leverage modern frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js to create more complex and interactive features.
One key attribute of web apps is their adaptability. Thanks to responsive web design, web apps can adjust their layout and functionality depending on the device, screen size, and orientation. This adaptability makes them a cost-effective choice for businesses seeking to reach a wide audience across multiple types of devices.
If you're interested in the potential possibilities of building a web app and would like to explore a potential use case, make sure to check out our case study on how we worked with Plus to build a well-being platform for young people utilising AI technologies.
There are three types of web apps:
Traditional Web Apps.
These are the most common type of web apps, delivering web pages on user requests. Every time a user clicks a link or a button, a new request is sent to the server, which responds with the appropriate HTML page.
Single-Page Apps (SPAs).
These apps dynamically rewrite the current web page with new data from the web server, eliminating the need for default page reloads. This provides a smoother user experience similar to a desktop application.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs).
PWAs combine the features of traditional web apps and native mobile apps. They can work offline, send push notifications, and even be installed on a device's home screen, just like a native app. They provide an app-like experience on the browser, enhancing user engagement.
In summary, web apps are an efficient way for businesses to ensure their digital offerings are accessible to a broad audience. The decision to use a web app should consider the nature of the app, target audience preferences, and business objectives.
The Pros and Cons of Developing Web Apps for Business.
The choice between mobile and web apps is a pivotal decision in your business's digital strategy. To help you make an informed choice, let's explore the pros and cons of web app development for your business.
What are the Pros of Developing a Web App?
- Cost-Efficient: Since web apps are not platform-specific, the same codebase works across different operating systems. This leads to a faster, more cost-effective development process compared to mobile app development.
-
Easy Updates: Changes and updates to web apps are straightforward and immediate. Users do not need to download updates, as they do with mobile apps. Any modifications are made on the server, and users can access the updated version upon reloading or during their next visit.
-
Broad Accessibility: Web apps can be accessed from any device with an internet connection and a web browser, offering a broader reach compared to mobile apps that need to be downloaded and installed.
-
No App Store Approval: Web apps do not need to go through the sometimes stringent approval process required by the app store, saving time and allowing for more frequent updates and changes.
What are the Cons of Developing a Web App?
- Limited Functionality: Web apps cannot leverage device features to the same extent as mobile apps. While advancements like Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are narrowing the gap, access to device functionalities like GPS, camera, and push notifications can still be limited.
-
Internet Dependency: Unlike mobile apps, most web apps require an active internet connection to function optimally, which might limit their usage in areas with poor or no internet connectivity.
-
Less Personalised User Experience: While web apps can offer personalisation to a certain extent, they typically do not provide the same level of personalised user experience as mobile apps.
-
Visibility: Web apps do not have the visibility provided by app stores. Users need to know the specific URL or the app needs to appear in search engine results, which requires effective SEO strategies.
To summarise, web apps are a viable solution for businesses seeking a cost-effective, universally accessible application that's easy to maintain and update. However, depending on your specific needs and the nature of your app, you may need to consider web apps' limitations in terms of device feature integration and user experience. As with any business decision, understanding your audience, their preferences, and your business objectives is paramount.
Enjoying what you're reading?
See our workConsiderations for Choosing Between Mobile Apps and Web Apps.

We've looked at what mobile and web apps are good at, and where they fall short. Now, you might be wondering: which should your business go for? It's not an easy question to answer. It depends on what your business wants to achieve, who your customers are, how much you can spend, and what you need the app to do. Let's look at some important factors to consider:
Security and Privacy Considerations:
Due to their proximity to the operating system and hardware, mobile apps can provide robust security measures, ensuring enhanced app security, however, this comes with the responsibility of frequently updating these measures to counter evolving threats. Web apps also offer substantial security features. Being online-based, though they might be more vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. Therefore your decision in this context may depend on the nature of your business, the level of app security you require and the sensitivity of the data you handle.
Performance and User Experience:
Mobile apps generally excel in performance and speed, offering a more fluid user interface and user experience (UI/UX). They also tend to integrate better with the device's functions, which can enhance the overall interaction and engagement of the user. Web apps, however, are more accessible because they're platform-independent and don't require any downloads, unlike mobile apps that must be downloaded from an app store. This cross-platform accessibility makes web apps a compelling choice for businesses targeting a broader demographic.
Business Objectives:
The first step is understanding what you want your app to achieve. A mobile app might be the better choice if you need an application that leverages device-specific features, delivers personalised experiences, or functions offline. On the other hand, if your goal is to reach as many users as possible with minimal development costs and you don't require extensive device features, a web app could be the way to go.
Budget and Time:
Mobile apps, especially native ones, typically take longer and cost more to develop due to their platform-specific nature. If budget or time constraints are a concern, a web app or even a cross-platform mobile app might be more suitable. Web apps can be more cost-effective and quicker to develop because they use a common code base for all platforms. However, the cost will depend on the complexity of the app, its features, and any customisations.
Revenue Generation.
The type of app you choose, mobile or web, can have a big impact on how you make money. Mobile apps can earn revenue from paid downloads, in-app purchases, subscriptions, and advertising. Web apps, on the other hand, generally make money from subscriptions, advertising, and freemium models where basic features are free, but users pay for premium services. The best choice for you depends on your business goals, resources, the features your app offers, and what your target audience is willing to pay for.
App Scalability.
App scalability, or the ability of your app to handle growth, is a key consideration when choosing between mobile and web apps. Mobile apps can be more complex to scale, requiring optimisation and potential architectural changes to handle more users or features, especially across multiple platforms like Android and iOS. Conversely, web apps typically offer simpler scalability, with changes such as server upgrades or back-end optimisations applied universally. Thus, understanding how your app will need to grow and adapt is crucial when making your decision.
App Maintenance and Updates.
App maintenance is a crucial consideration in the mobile app vs. web app debate. Mobile apps, especially those developed for both Android and iOS, can be more demanding in terms of updates and maintenance. Each update needs to be pushed to the app stores, and users must download these updates to benefit from them. Web apps, on the other hand, have a more straightforward maintenance regime. Changes can be made directly to the server, and users will get the updated version upon their next visit, with no need for manual updates.
To conclude, the choice between a mobile app and a web app is a strategic decision that should align with your business's unique needs and objectives. It's not uncommon for businesses to eventually end up with both, each serving a specific purpose in their digital strategy. When in doubt, consulting with an experienced software development agency can provide valuable insights tailored to your business scenario.
Our Final Thoughts.
In a nutshell, the choice between a mobile app and a web app isn't a one-size-fits-all scenario. It's about what works best for your business, your customers, and your goals. You might even find that a combination of both could be the key to satisfying your digital needs and engaging your audience effectively.
And remember, your decision should be based on your specific objectives, user preferences, budget, and the functionality you aim to provide. Both mobile apps and web apps have their strengths and weaknesses, but understanding these will guide you to the right choice.
At our software development agency, we’re passionate about creating both high-performance mobile apps and efficient web apps. We’ll help you weigh these factors and make the best decision for your business, aligning it with the latest market trends and customer behaviour patterns.
Whether you're considering mobile or web apps for your business, remember that choosing the right development partner is as crucial as choosing the right platform. Reach out to us to discuss your project and learn how we can help you maximise your ROI and enhance your competitive advantage in the digital landscape.
